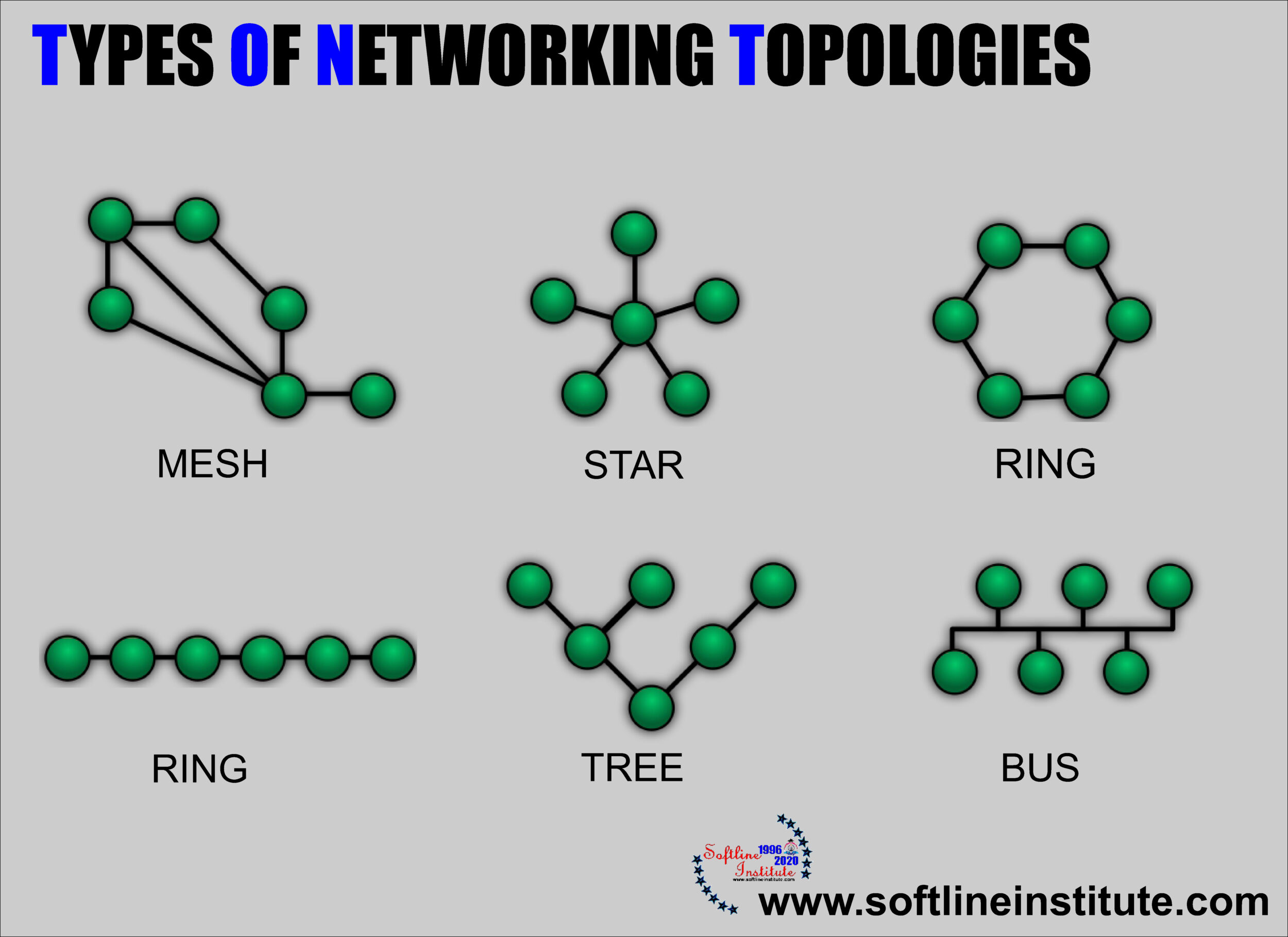
Topologies are the way networks are physically connected together. Topology determines the complexity and therefore the cost of network cable installation. Cable installation can often be a major cost factor for network system. Topology also determines the strategy for physically expanding the network. Different way in which computers may be connected together are described in the following subsections.
Linear Bus Topologies
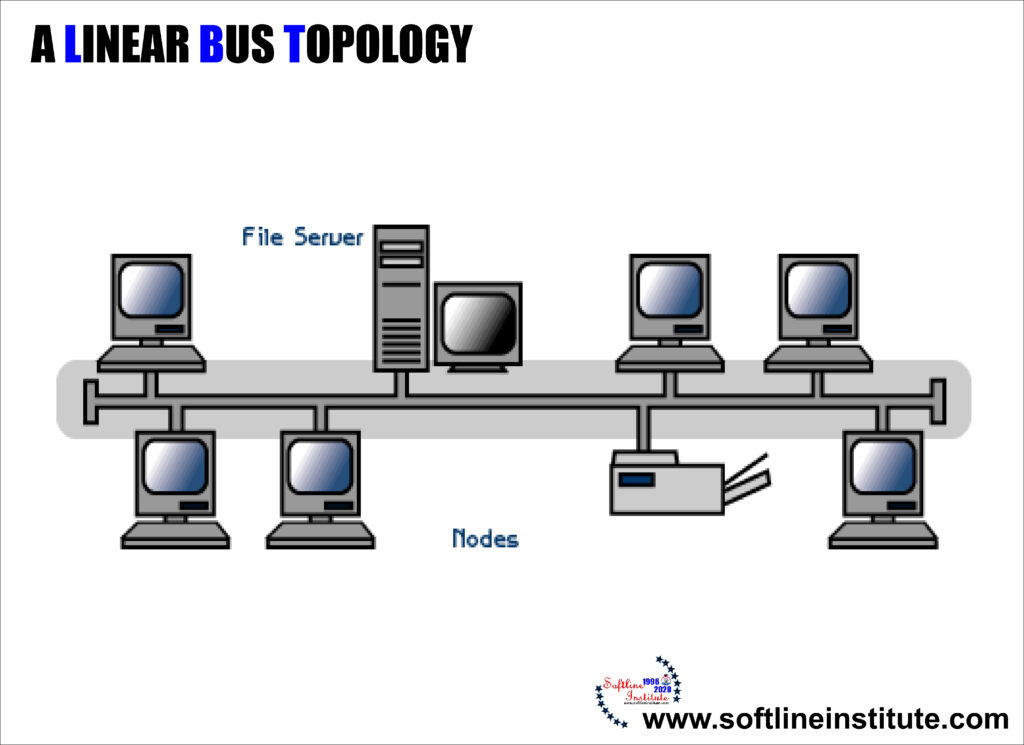
In this layout, a single main cable connects each node, in what amounts to a single line of computers accessing it from end to end. Each node is connected to two others except the machines at either end of the cable, which are connected only to one other node. The network operating systems keeps track of a unique electronic address for each node manages the flow of data based on this addressing scheme.
Linear Bus topology has the advantage of not requiring that every computer be up and running in order for the network to function. But because a single cable is dedicated to all the information traffic, performance can be slow at times. This topology is often found in client/server systems, where one of the machines on the network is designated as a file server meaning that it is dedicated solely to the distribution of data files and it is not usually used for information processing.
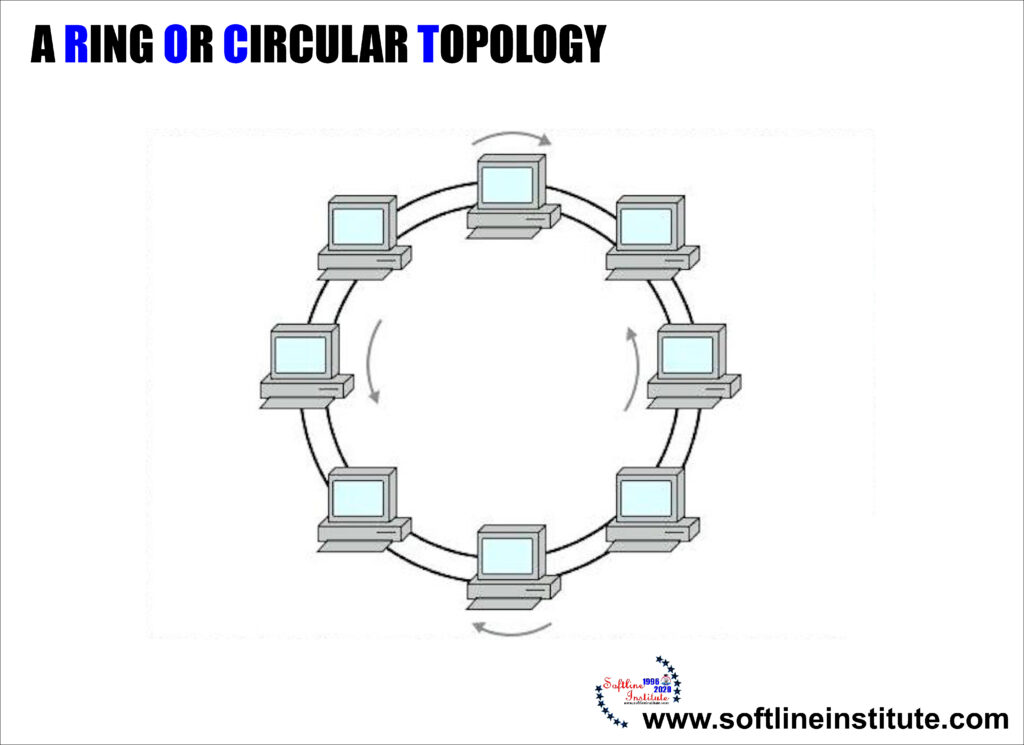
CIRCULAR
This layout is similar to the linear bus, except that the nodes are connected in a circle using cable segments. In this Layout, each node is physically connected to only two other. Each node passes information along to the next, until it arrives at its intended destination. Performance is faster on this system because each portion of the cabling system is handling only the data flow between two machines. This type of topology can be found in peer-to-peer networks, in which each machine manages both information processing and the distribution of data files.
STAR TOPOLOGIES
Each node is connected to a single, centrally located file server, using its own dedicated segment of cable. This topology has the advantage of minimum data traffic along the cables (node to server only), thus providing optimum performance. But because a single machine must co-ordinate all the data communications, this topology requires an extremely powerful and expensive file server.

This is a network topology containing zero or more nodes that are linked together in a hierarchical fashion. The topmost node is called the root. The root may have zero or more child nodes, connected by edge (links); the root is the parent node to its children. Each child node can in turn have zero or more children of its own. Nodes sharing the same parents are called siblings. Every node in the tree has exactly one parent node. All nodes in the tree are descendants of the root node. These relationships ensures that there is always one and only one path.

Graph
In this method of connection, zero or more nodes are linked together in an arbitrary fashion. Any two nodes in a graph may (or may not) be connected by link. Not all the nodes in a graph need to be connected. But if a path can be traced between any two nodes, the graph is a connected one.
FOR MORE INFORMATION